CRISPR/Cas9 is a new method for targeted genetic changes. Together with other methods, it is part of the so-called genome editing toolbox. At the moment, genome-editing is mostly discussed in the context of medical applications, but its use is perhaps even more promising for plant breeding. Scientists from China, the United States and Germany, among them Prof. Dr. Detlef Weigel of the Max-Planck-Institute for Developmental Biology in Tübingen, have now proposed a regulatory framework for genome editing in plants that has been published in the journal Nature Genetics.
Using genome editing, DNA can be altered in a very precise manner. Often, only a single base, that is one letter of the genome, is replaced or deleted. This is essentially the same as the constantly occurring genome changes in nature due to random mutations. After such a mutation or genome-editing have taken place, their consequences are indistinguishable. This is not due to technical shortcomings, but to the factual lack of physical, chemical or biological differences. “We thus do not see a reason for considering genome edited plants as genetically modified organisms”, says Weigel. The changes resulting from genome-editing should however be analysed and documented to ensure that no remnants of foreign DNA, if such an approach was used for genome editing, are left behind. Apart from that, plants changed in this way should not be subject to stricter rules than conventionally bred plants.
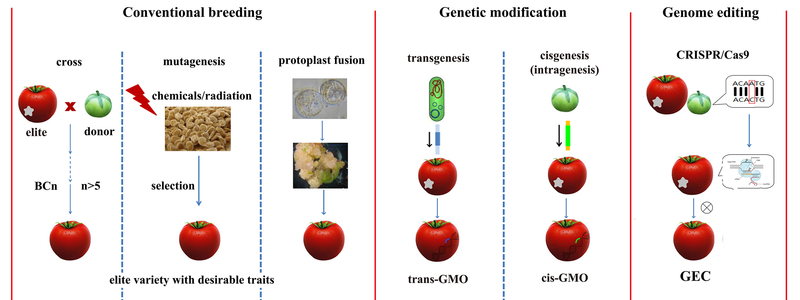
The aim of plant breeding is to continually improve advantageous traits in order to make our crops more resistant against fungal infection, to help them cope better with drought or to thrive with less fertilizer. One way to reach this goal is to cross cultivars with different advantageous traits. As an alternative, chemicals or radiation are deployed, both of which cause randomly distributed mutations throughout the genome. Unfortunately, for both techniques a large portion of the resulting offspring is not better or even worse than the parental plants, and finding promising individuals is often lengthy and tedious. Both techniques are among the standard tools of conventional breeding, whose products can enter the market without authorization.
For several decades, it has been possible to insert genes into plants, using genome engineering methods. These could be genes coming from other plants, or from completely different organisms such as bacteria. A disadvantage of these techniques is that it cannot be controlled where exactly in the genome the new genes get inserted. Thus many candidates have to be scrutinized until a plant with the desired traits is found.
In reports of genome editing, metaphors such as genome surgery or genetic scalpel are often used. “Conventional genetic engineering can be compared to open-chest surgery” illustrates Weigel, while genome-editing would correspond to minimally invasive surgery, because one can precisely determine where in the genome a change is supposed to happen. Using genome engineering methods one can also precisely replace genes of one species with genes of other varieties or close relatives – which is one goal of conventional breeding as well. Genome-editing allows to achieve the same alterations as conventional breeding, but much faster.
For these reasons, the scientists advocate the following common sense approach concerning the development and authorization of genome-edited plants: First, the risk of uncontrolled spread should be minimized during the development phase. Second, the resulting DNA-changes should be precisely documented. Third, it has to be taken into account that CRISPR/Cas9 techniques may in the beginning require insertion of foreign DNA into the cell; if this is the case, it has to be documented that the foreign DNA has been completely removed. Finally, has a gene been replaced by one from a different species, it should be stated how close the two species are related to each other. Are they only distantly related, additional case-by-case considerations might be necessary. For registration of new varieties, documentation regarding these points should be included, but otherwise, genome edited plants should be treated like conventionally bred varieties.
The European Union has not finalized their assessment, but in both Germany and Sweden the responsible authorities have already declared, that certain genome-edited varieties are in principle the same as products of conventional breeding. “An important aim of breeding is to make agriculture more sustainable. Genome editing can, for example, help when breeding for resistance to fungal infection without the use of chemical pesticides. We should not miss out on such opportunities,” states Weigel.
Original Publication
A proposed regulatory framework for genome-edited crops. Nature Genetics.
DOI 10.1038/ng.3484
Contact
Prof. Dr. Detlef Weigel
Phone.: 07071 601-1410
E-mail: detlef.weigel@tuebingen.mpg.de
About the Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology
The Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology conducts basic research in the fields of biochemistry, genetics and evolutionary biology. It employs about 350 people and is one of four Max Planck Institutes located at the Max Planck Campus in Tübingen. The Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology conducts basic research in the areas of biochemistry, molecular biology, genetics, cell- and evolutionary biology. It does not develop genetically modified crops. It is one of 83 research institutes that the Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science maintains in Germany.
Source
Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, press release, 2016-01-28.
Supplier
European Union
Max-Planck-Institut für Entwicklungsbiologie
Nature Genetics
Share
Renewable Carbon News – Daily Newsletter
Subscribe to our daily email newsletter – the world's leading newsletter on renewable materials and chemicals









